In a buck converter cicuit, the output capacitor will determine the output ripple voltage. Having a big output capacitor at the output can lower the ripple voltage which is good but oversizing the capacitor can be bad at the same time. It cost more money, needs a bigger layout and it is not compact anymore.
The value of the capacitor can be determined using an equation derived from the capacitor waveform at the steady state.
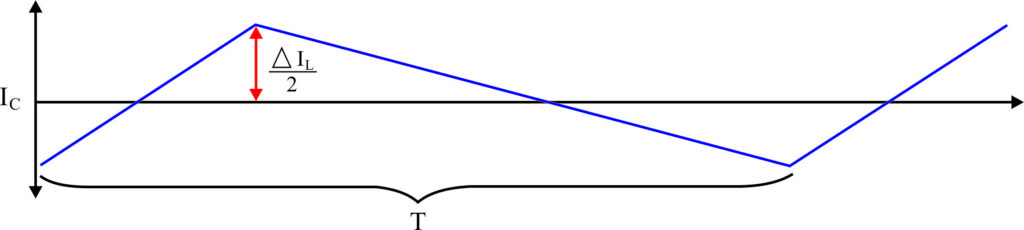
The area below the waveform is equal to the amount of the charge on the capacitor. Based on that, we can write the equation of the capacitor charge mathematically.
After reaching the steady state the AC component (ripple) of the inductor will flow through the capacitor
while the average inductor current will flow through the load. Because of this, the “capacitor current will equal to half of the inductor ripple current“. As we can see from the Figure above.
![]()
![]()
So far, we can calculate the amount of charge which is equal to the area below the waveform. Now, we will rearrange this equation in order to calculate the capacitor value.
![]()
![]()
VOUT is the output voltage of the buck converter.
L is the inductor value.
fSW is the switching frequency of the power MOSFET.
ΔVOUT is the output ripple voltage.
Based on the known parameters now we can determine the minimum capacitor value to meet the output ripple voltage.