On a buck converter circuit, the value of the inductor will determine the output ripple current. One way to determine this value is by calculating the area below the rising slope or falling slope of the inductor current waveform.
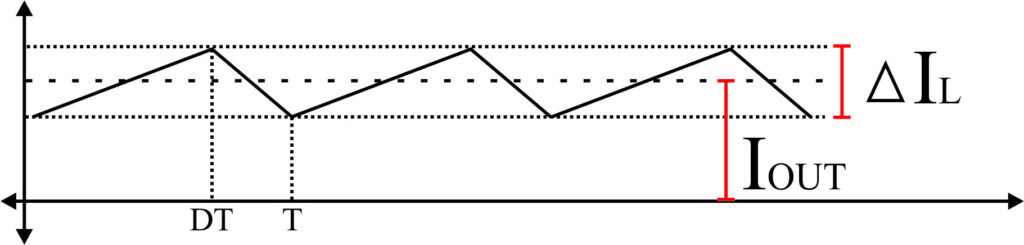
The figure above illustrates the inductor current waveform operating in CCM mode (Continuous Conduction Mode) in the steady-state condition.
ΔIL is the ripple current that we want on the inductor.
D is the duty cycle of the switching MOSFET.
T is the period of the switching (fSW)cycle of the Buck converter.
![]()
![]()
The first equation is a formula to calculate the triangle area below the current waveform. Based on this equation we can rearrange the equation to calculate the inductor value based on the ripple current (ΔIL), the switching frequency (fSW), and the input (VIN) and output voltage (VOUT).
This equation is only valid if we assume the inductor current doesn’t reach zero at the end of a switching cycle.
Now, with these known parameters we can go to the electronic component distributor’s website and look for the available inductor based on the parameters we want.